Run Boltz-2 Online For Free
Boltz-2 is an open-source model that predicts the structure of biomolecular complexes from simple inputs. Specifically, Boltz-2 can be used to predict:
- Single-protein structures.
- Multi-protein complexes, including antibody–antigen complexes.
- Protein–small molecule complexes with estimates of binding affinity.
- Complexes between proteins and peptides, even cyclic peptides.
- Protein–nucleotide complexes.
For scientific and architectural details about how Boltz-2 works, see our Boltz-2 FAQ; for external benchmarks of Boltz-2, see our benchmarks page.
The versatility of Boltz-2 makes it a useful tool for a variety of scientific applications, including building structural models, screening potential binders, designing new enzymes, and much more. Additionally, Boltz-2 is available under the open-source MIT license, so it can be used for commercial applications (unlike some competing models).
Unfortunately, using Boltz-2 directly via command-line interface or Python scripts requires users to write their own software, obtain GPUs to run the calculation on, parse the output files, and so on. Taken together, these technical requirements make it challenging for many life scientists to run Boltz-2 themselves. (See our guide to running Boltz-2 calculations.)
Running Boltz-2 Online
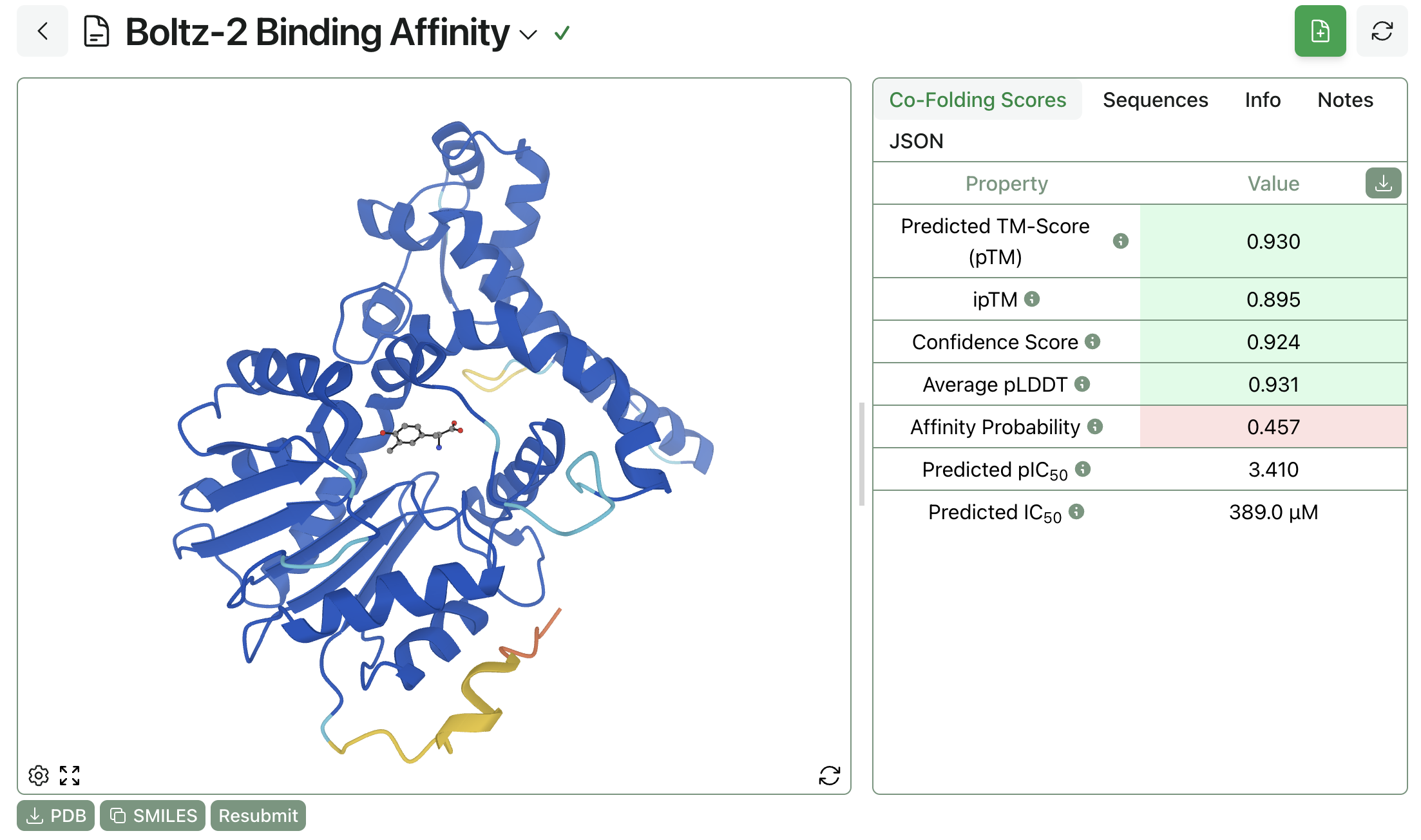
Rowan's cloud computational-chemistry platform makes it easy for any scientist to start running Boltz-2 calculations. Users can directly input sequences (for biopolymers) or SMILES representations (for small molecules), specify any geometric constraints, and tune other advanced parameters (like number of samples or inference-time steering).
Once submitted, jobs run on dedicated high-performance cloud hardware and stream results directly to the browser. The finished structures can be viewed through Rowan's 3D viewer or downloaded as .PDB files for local processing.
Running Boltz-2 through Rowan has several advantages:
Secure Inference
While many Boltz-2 implementations use public MSA servers, Rowan hosts our own secure multiple-sequence alignment (MSA) server to make sure that users' data is never leaked to a third-party. Structures submitted to Rowan are confidential and cannot be viewed by other users or by Rowan (unless explicitly shared).
Graphical Interface
Rowan makes it easy to view Boltz-2 results in an intuitive and easy-to-understand way. Users can change which atoms are displayed, zoom in on the ligand or zoom out to see the entire protein, and see color-coded confidence metrics like iPTM, pLDDT, and confidence score, making it easy to get scientific insights right away.
Physical Validity
Rowan automatically runs a suite of structural checks on structures generated by Boltz-2, including stereochemistry checks, PoseBusters analysis, and (optionally) ligand strain calculations. These additional checks can be used to detect anomalous Boltz-2 predictions or highlight dubious predictions, helping scientists have confidence in the validity of their results.
Easy Resubmission
Structures generated by Boltz-2 can be resubmitted to any other Rowan workflow, including:
- Molecular dynamics
- Membrane permeability
- Solubility
- Docking
- Or co-folding with a different model
If you want to integrate Boltz-2 predictions into a larger computational workflow, Rowan makes it easy to do so.
API Access
Boltz-2 calculations can also be submitted through Rowan's free Python API:
import rowan
workflow = rowan.submit_protein_cofolding_workflow(
initial_protein_sequences=[
"MENFQKVEKIGEGTYGVVYKARNKLTGEVVALKKIRLDTETEGVPSTAIREISLLKELNHPNIVKLLDVIHTENKLYLVFEFLHQDLKKFMDASALTGIPLPLIKSYLFQLLQGLAFCHSHRVLHRDLKPQNLLINTEGAIKLADFGLARAFGVPVRTYTHEVVTLWYRAPEILLGCKYYSTAVDIWSLGCIFAEMVTRRALFPGDSEIDQLFRIFRTLGTPDEVVWPGVTSMPDYKPSFPKWARQDFSKVVPPLDEDGRSLLSQMLHYDPNKRISAKAALAHPFFQDVTKPVPHLRL"
],
initial_smiles_list=["CCC(C)CN=C1NCC2(CCCOC2)CN1"],
name="Boltz-2 Workflow Submitted Via API",
model="boltz_2",
ligand_binding_affinity_index=0,
)
print(f"View results privately at https://labs.rowansci.com/protein-cofolding/{workflow.uuid}")
workflow.wait_for_result().fetch_latest(in_place=True)
print(workflow.data)
Run Boltz-2 on Rowan Today
It's easy to get started running Boltz-2 calculations on Rowan! Simply create a free account, navigate to the "Protein–Ligand Co-Folding" workflow, and submit your first calculation. All Rowan users get 500 free credits upon account creation, so you can try out Rowan's Boltz-2 predictions for free.